

‘I haven’t anyone in mind,’ Matthew said. ‘I’m thinking of getting married,’ Matthew said. Demonstration of Cohesion in action Consider the cohesion and coherence in the following dialogue: 1. Instead, you would compute the FFT over 2-second intervals, and compare the phase differences between two channels at that Fourier coefficient across the distribution of 2-second intervals. Cohesion refers to the many ways (grammatical, lexical, semantic, metrical, alliterative) in which the elements of a text are linked together. Cohesion is objectively identifiable coherence is far more subjective, depending on the reader/listener’s interpretation. Even if you are considering only a single Fourier coefficient, because of temporal nonstationarities, it doesn't make sense to compute one Fourier coefficient over an entire recording of, say, 10 minutes. Those two oscillators can be synchronized, desynchronized, or transiently synchronized. It's certainly simpler to compute, and it's easy to refine the sampling along the frequency axis. Therefore, you would filter from 8-12 Hz, and then there will be frequency fluctuations over time between the two channels (or, more generally, two oscillators). If the intuition that correlation looks for similarity in time and coherence looks for similarity in frequency is correct, then you might be better off sticking to the time-frequency plane. Inversely, values of correlation coefficients close to one are interpreted as perfect synchrony, while low values or those indistinguishable from 0 are commonly interpreted as weak or 0 spike cross correlations. But a single Fourier coefficient is not really interpretable in brain data. The correlation coefficient is equal to one if the spike trains are identical, and it is 0 if the spike trains are independent. I know that in engineering and digital signal processing, the magnitude squared coherence is a measure of phase correlation between two signals defined as the. So, if you would extract a single Fourier coefficient from two channels, then over time, the phase difference is trivially stationary, as you noted. Taylor & Francis publishes knowledge and specialty research spanning humanities, social sciences, science and technology, engineering, medicine and. Coherence bandwidth is a statistical measurement of the range of frequencies over which the channel can be considered 'flat', or in other words the approximate maximum bandwidth or frequency interval over which two frequencies of a signal are likely to experience comparable or correlated amplitude fading. It makes sense to talk about "alpha" as energy between ~8 and ~12 Hz, but it doesn't really make sense to talk about energy at 11.23442 Hz. That's why we talk about frequency bands instead of precise frequencies. We can develop the FFT of these time histories, and relate the "frequency" of each "bin" by the expression "frq[i := f.sampling * i /N.samples".The key insight is that neural signals are highly non-stationary (with some constraints). However, coherence remains relatively stable. I have two data vectors, samples taken at a fixed sampling frequency for a given length of time. Correlation varies widely (between 0 and 1) for differences in phase lag.
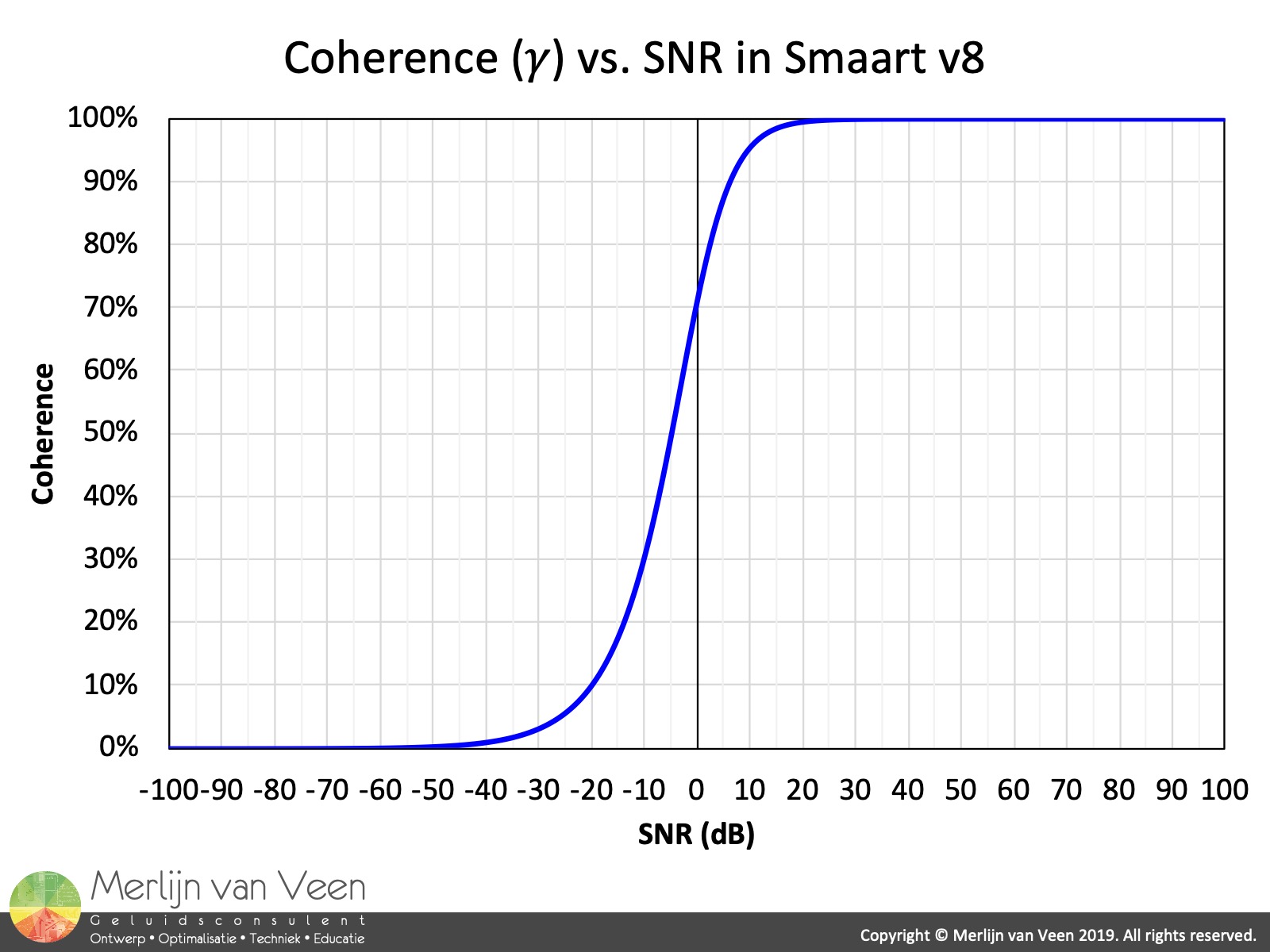
That, as I understand it, is the usefulness of the coherence function to determine if two signals share a causal relationship. We look at coherence (on a spectrum analyzer this is a "built-in" function) to see how much of the acceleration measured is due to the force applied if there happens to be another force that's creating the acceleration then the coherence will be low, if the acceleration is due mostly to the force, the coherence will be high (close to 1.) If I have an exciter at a fixed frequency (a rotating shaft)the coherence of an accelerometer with that frequency will be high, and it will be low at other frequencies because the exciter isn't putting any power into those frequencies. as on thermodynamic and correlation properties near equilibrium points of. We normally look at the transfer function (or frequency response function), so much force produces so much acceleration at a given frequency. FUNDAMENTAL PROBLEMS OF QUANTUM CRITICAL PHENOMENA Luigi De Cesare' and Dimo. correlation or first order coherence function. They happen (this time) to be measurements from two accelerometers on a structure, more often they are a force measurement (from a "shaker") and an accelerometer. and creation operators (or c-numbers in a classical field), and E0 is the electric field per photon. the correlations between the spectral content of both signals. >Fred coherence (Y1,Y2,n,r,W) is a "local computing the power spectral density and the coherence of synthetic and experimental. The magnitude-squared coherence enables you to identify significant frequency-domain correlation between the two time series.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
